Neon54 Avis : Arnaque ou Fiable ?
Neon54 : tout ce que vous devez savoir !
De nos jours, les casinos en ligne poussent comme des champignons, à tel point que l’on n’arrive plus à savoir où donner de la tête ! Il est, en effet, très difficile de faire confiance à un site au détriment d’un autre, sans avoir une preuve tangible de sa fiabilité et ce fait peut être problématique pour les utilisateurs qui souhaiteraient se lancer dans une nouvelle aventure !
Neon 54 fait partie des sites de jeux d’argent que nous avons testés et nous pouvons désormais vous en donner un avis clair et neutre.
Que savons-nous du casino en ligne Neon54 ?
Neon 54 est un casino en ligne très récent, crée en 2021. Crée par le groupe Rabidi N.V, Il reste encore très méconnu du public mais il est en train de gagner beaucoup de popularité et de confirmer sa place sur le marché.
Il détient une licence de jeu à Curaçao et peut se vanter d’avoir un ensemble de systèmes de sécurité très avancé.
Disposant d’une ludothèque très riche, il entend faire profiter ses clients d’une expérience plus qu’intéressante en leur faisant gagner un maximum d’argent.
Vous avez envie d’avoir plus d’informations sur l’utilisation de cette plateforme ? Lisez la suite de notre test.
| 🥇 Bonus | 1000€ |
| 📅 Création | 2021 |
| 💻 Site | Neon54 |
| ⭐ Note | 9.6 |
Comment utiliser Neon54 ?
Pour avoir accès aux jeux de Neon54, vous devez d’abord vous inscrire sur le site, comment ? En suivant notre petit tuto.
Comment s'inscrire sur Neon54 ?
L’inscription sur Neon 54 se fait de manière rapide et très simple. Pour devenir membre du casino, vous devrez juste suivre les étapes ci-dessous :
- Une fois sur le site officiel de la plateforme, cliquez sur l’onglet “créer un nouveau compte”.
- Remplissez le formulaire d’inscription disponible sur la page d’accueil, en indiquant votre nom, adresse, e-mail, devise souhaitée, pays.
- Confirmez votre inscription pour obtenir le bonus de bienvenue.
- Dès que vous aurez effectué le premier dépôt (d’au moins 20 euros), vous pourrez commencer à placer des paris sur le site.
Les méthodes et dépôt et de retrait sur Neon 54
Nous avons été agréablement surpris de voir que le casino autorisait autant de méthodes de paiement car ceci est à l’avantage des utilisateurs qui auront plus de moyens pour déposer ou retirer de l’argent sur leur compte. Nous avons aussi apprécié la simplicité de ces deux opérations.
Les dépôts sur Neon54 :
La communauté de Neon 54 aura la chance de disposer d’un grand nombre de moyens de paiement qui vous sont listés comme suit :
- Mfinity
- Volt
- Ripple
- Visa
- MasterCard
- Bitcoin
- Ethereum
- Litecoin Virement bancaire
- Skrill
- Paysafecard
- EcoPayz
- Neteller
Pour déposer de l’argent sur votre compte,
- Rendez-vous sur le site du casino en ligne.
- Cliquez sur l’onglet “paiements” pour accéder à la page concernée.
- Sélectionnez le pays et la monnaie souhaitée parmi celles proposées sur la plateforme.
- Entrez le montant que vous voulez déposer et cliquez sur « Déposer ».
- Confirmez l’opération pour que le dépôt arrive immédiatement sur votre compte.
Les retraits sur Neon54 :
Pour le retrait, les méthodes autorisées sont également très nombreuses. Vous pouvez donc utiliser votre carte Visa, Mastercard comme vous pourrez opter pour le Virement bancaire ou Skrill.
Vous avez enfin remporté le gros lot que vous espériez tant ? Nous sommes ravis pour vous! Mais savez-vous comment vous y prendre pour retirer vos gains ?
Si ce n’est pas le cas, suivez nos consignes pour le faire :
- Aller sur la page des paiements.
- sélectionnez votre pays et votre monnaie.
- Cliquez à présent sur “retraits”.
- Choisissez une méthode de retrait sur la liste dont nous avons parlé ci-dessus. (Celle-ci correspondra automatiquement à celle de vos dépôts).
- Confirmez le montant de votre retrait.
- Recevez votre argent dans les plus brefs délais.
Les bonus et promotions sur Neon 54
Vous n’êtes pas encore convaincu par Neon 54 ? Laissez-nous vous présenter sa gamme de bonus et promotions et vous aurez vite fait de changer d’avis ! Voici donc les surprises auxquelles vous aurez droit en choisissant ce casino en ligne plutôt qu’un autre :
Le Bonus de bienvenue
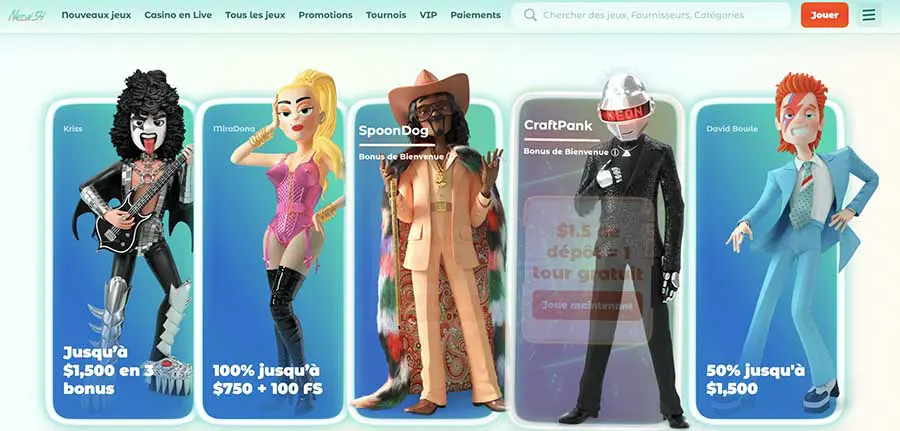
Pour vous inscrire sur Neon 54, vous devrez choisir un des personnages présents sur la page d’accueil afin de bénéficier d’un package complet sans avoir à entrer un code promo.
Les personnages en question sont
- Kriss qui vous offrira 1000 euros de bonus sur vos trois premiers dépôts.
- Spoondog avec qui vous gagnerez 10% de cashback jusqu’à 200 euros
- MiraDona qui vous propose 100% de bonus jusqu’à 500 euros +100 free spins et un bonus Crab.
- Craft Pank qui vous fera profiter d’un bonus allant jusqu’à 500 tours gratuits.
- David Bowle avec un bonus de 50% jusqu’à 1000 euros.
Le Programme VIP de Neon54
Dans le but de récompenser ses clients les plus fidèles, le casino a prévu un programme très généreux. Ces derniers auront droit à des points de fidélité les aidant à gravir les différents échelons et acquérir des statuts supérieurs et ce, tout au long des leurs mises et de leurs dépôts.
C’est un dispositif complet permettant aux joueurs de profiter de plusieurs avantages les favorisant par rapport aux autres utilisateurs. Ils auront également des bonus exclusifs.
Par ailleurs, pour devenir un joueur VIP de Neon 54, participez au programme mis en place par le site et augmentez votre solde au fur et à mesure que vous jouerez à vos jeux favoris.
Bien entendu, les récompenses offertes, suite à ce nouveau statut, comprennent des bonus, des cadeaux, des bons d’achats et bien d’autres!
Promotions diverses sur Neon54
Tout au long de la semaine, vous pourrez gagner de grosses promotions que vous pouvez consulter sur la rubrique indiquée sur le site. Voici de quoi il s’agit :
Bonus hebdomadaire
C’est un bonus de 50 free spins que vous recevrez dès lundi, suite à votre premier dépôt de la semaine qui sera obligatoirement de 20 euros minimum.
Le cashback hebdomadaire
Cette promotion concerne les joueurs VIP du 3ème, 4ème et 5ème niveau auxquels elle permet d’obtenir, chaque lundi, un cashback de 15% et 3000 euros.
Le cashback en direct
Tous les dimanches, et en tant que fan de jeux en direct, vous recevrez 25% de bonus cashack sur vos pertes jusqu’à 200 euros, tous les dimanches.
Le bonus Week-end
Lorsque vous effectuez votre premier dépôt du week-end, vous gagnez un bonus de 50% jusqu’à 50 euros + 50 tours gratuits.
Le service client de Neon54
Pour se rapprocher davantage de ses utilisateurs, le casino a mis en place un service d’aide disponible 24 h/24, 7 jours sur 7 et en plusieurs langues. Vous pouvez donc joindre ses équipes à n’importe quel moment, en cliquant tout simplement sur le bouton “ contactez-nous” sur n’importe quelle page Web.
Voici les canaux de communication via lesquels vous pouvez contacter le service client Neon :
Le Chat en direct
En allant sur le site du casino, vous pourrez chatter en direct avec des conseillers expérimentés qui n’hésiteront pas à vous prêter main forte. De cette manière, vous obtiendrez une réponse instantanée à toutes vos interrogations.
Par Email
Vous avez la possibilité de demander des explications aux opérateurs du casino, en leur envoyant un message par mail à l’adresse : à support@neon54 tous les jours. Expliquez-leur clairement votre problème et vous aurez un retour dans les 45 minutes.
La Foire aux questions
Vous avez un souci avec votre compte ? Vous ne savez pas comment vous inscrire sur la plateforme ? Vous avez envie d’en savoir plus sur les bonus et les promotions proposés par Neon 54 ? Consultez la FAQ et vous aurez toutes les réponses dont vous aurez besoin à travers les échanges des utilisateurs.
Les jeux et les fournisseurs de Neon54
Neon 54 possède l’une des ludothèques les plus riches qui existent actuellement. Avec un large panel de machines à sous, plus de 1000 jeux de différentes catégories et des fournisseurs haut de gamme, on peut dire que les développeurs se sont vraiment donné les moyens pour vous donner le meilleur du jeu !
Les machines à sous
On ne peut parler de ludothèque « bien garnie », sans citer les machines à sous ! C’est, en effet, le jeu le plus dominant de la plateforme. Les thèmes sont aussi variés ; Il y en a vraiment pour tous les goûts : La magie, l’Égypte, le monde fantastique, les fruits, et bien d’autres encore.
Les fournisseurs de ces jeux sont très connus à l’échelle mondiale. Parmi eux, nous vous recommandons Play’N Go et Pragmatic, Yggdrasil, Netent, Micrograming, Evolution Gaming, etc.
Si vous recherchez les dernières sorties ; vous pourrez les trouver sous “ nouveaux”. Il existe également une autre catégorie pour les plus populaires et les meilleures machines à sous.
Le seul bémol, ce serait le manque de filtrage !
Les jeux de table et live chez Neon54
Pour les jeux de table, Neon 54 collabore avec Évolution Gaming, pour vous obtenir les plus belles offres de jeu dont le blackjack, la roulette, le baccarat et cela, en direct et avec de vrais croupiers.
Vous avez aussi le choix de jouer en direct au Monopoly Live ou au Crazy Time.
Les autres jeux chez Neon54
Jackpot
Ils font partie des jeux les plus favoris car ils proposent de gagner de véritables fortunes (plus de 21 000000 euros).
Mini Jeux
En partenariat avec le fournisseur Spribe, célèbre pour son jeu Aviator, le casino entend faire plaisir à ses clients de la meilleure des façons !
Ces jeux comprennent des mini Plinko, Mines, Dice, Hilo, Keno, Goal et Mini Roulette.
Des jeux avec croupiers en direct
Les jeux avec croupiers en direct sont : Wheel of Fortune, Craps Live, Immersive Roulette, Lightning Dice, etc.
Les Avantages et Inconvénients du casino en ligne Neon54
Résumons notre test en énumérant les avantages et les inconvénients du casino dans les points ci-dessous :
Points forts
- Fiabilité et sécurité
- Diversité des moyens de paiement.
- Richesse de son offre de jeu.
- Intégration de jeux avec croupiers en direct.
- Des bonus et promotions très alléchants.
- Un excellent support client.
- Un design très attrayant.
- Facilité de navigation sur le site.
Points faibles
Le seul point faible de Neon 54 réside dans l’absence d’une application mobile.
Est-il possible de jouer à Neon54 sur mobile ?
La bonne nouvelle, c’est que Neon 54 s’adapte parfaitement au jeu sur mobile ou tablette. Il est vrai qu’il n’existe pas encore d’application mobile mais le casino compte sur la technologie HTLM5 pour offrir la chance à ses membres de jouer depuis un simple navigateur web mobile. Ainsi, ils pourront accéder à toutes les fonctionnalités, les jeux et les promotions en se servant d’une simple connexion 5G ou Wifi.
Avis sur le Casino en ligne Neon54 en vidéo

Bonus sur Neon54
Informations générales
- Nom: Neon 54
- Date de création : 2021
Dépôt et retraits
- Mise minimum: NA
- Dépôt minimum : 20 €
- Retrait minimum: 20 €